Although sailing downwind in the trades in a cruising boat has its challenges, it is a relatively pleasant and fairly easy experience on a catamaran.
There is a more-or-less continuous flow of air across the Atlantic called the trade winds. Because the Earth is warmer at the equator and colder at the poles, and because of Earth’s rotation, this flow is generally westerly (from the west) near the poles and easterly nearer the equator.
Every season there is a migration of cruising boats that follow the trades when the trade winds are steady. One such migration is from the Mediterranean to the Caribbean across the Atlantic Ocean in November / December every year from east to west. It is the same downwind route that we took when we sailed our own boat back from France to the Caribbean in November 2019.
Although sailing downwind in the trades in a cruising boat has its challenges, it is a relatively pleasant and fairly easy experience on a catamaran. Assuming that your catamaran is a regular production cat like a Leopard, Bali or Lagoon, well equipped with cruising gear, you’ll perform much the same way as an equivalent monohull with either a conventional symmetrical spinnaker or asymmetric sail. Like on monohulls, you will pretty much sail to hull speed provided your catamaran is not overloaded. Performance cats are a different animal of course.
Whether a monohull or multihull, sailing dead downwind doesn’t usually make great VMG (velocity made good), because the apparent wind speed (AWS) is 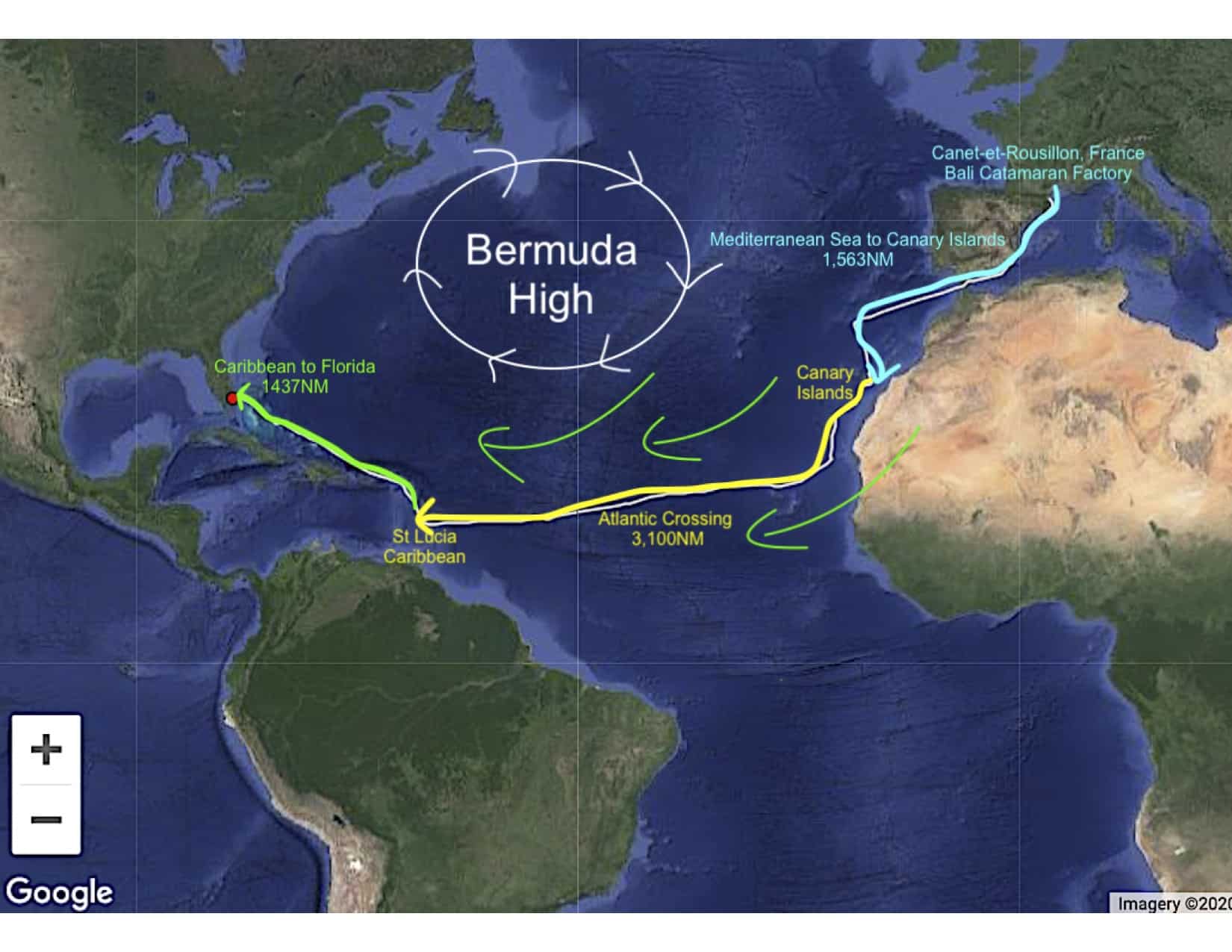 limited to true wind speed (TWS) minus your speed over the ground (SOG.) So, generating any apparent wind to help increase wind speed, is impossible.
limited to true wind speed (TWS) minus your speed over the ground (SOG.) So, generating any apparent wind to help increase wind speed, is impossible.
Therefor a regular cruising cat, much like a monohull, needs a lot of sail area and has to sail deep downwind if it is to achieve a decent speed made good (VMG), typically between 160° and 170°. But multihulls offer a unique wide platform for setting and sheeting downwind sails that set it apart from monohulls and make it a lot easier to sail downwind. The wide deck platform provides outboard sheeting points that makes downwind sails more efficient and the windward hull provides a tack location when sailing deeper angles is desired. Our preferred downwind sail is the assymmetrical spinnaker but a wing-on-wing configuration with dual head sails is very effective and, in many cases, safer and easier to handle for shorthanded crew.
Asymmetrical Sails for Downwind Sailing
Most modern catamarans choose to fly an asymmetric spinnaker and tack it to the weather bow. Sailmakers have managed to design these asymmetric sails so that they have more volume aloft. That means that even when you’re sailing deep angles, the luff of the sail sets well to windward and is able to catch more breeze that would have passed to windward of the boat. This configuration is pretty much as good as it gets for a cruising catamaran and is good for a range of apparent wind angles of between 90-160 degrees.
That was our sail plan onboard our Bali 5.4 when we did the Atlantic crossing…that is until we blew the asymmetrical sail halfway through our crossing and had to resort to using our Code Zero and jib in a wing-on-wing configuration for the duration of the trip. The spinnaker propelled us across the Atlantic fast. We easily did 200nm + days on the Bali 5.4 in 15 knots of wind.
The asymmetrical sail is a fantastic sail in light winds and once you understand just how easy it is to set and take down, it will be one of your favorite sails to use. These big downwind sails set forward of the mast and so, if there should be a sudden wind increase, the sheet can quickly be released, and the sail allowed to depower by streaming downwind. That means that when on passage, a cruising catamaran can always be rendered safe if things get a little out of hand. All being well, it can be snuffed, ideally while in the lee of the mainsail.
The key as always is in preparation. Make sure the sheets and halyard are all free to run and the sock is not crossed or tangled. The other mistake many of us tend to make is to over-sheet the spinnaker. One should let it fly out as far away from the boat as possible. It will make a huge difference. Keep easing the sheet until the luff curls, testing how far you can ease it out. You can always wind it back in. See the video here of how we set up our asymmetrical sail>>
We had our Asymmetrical sail made by Quantum in Annapolis, MD for our new Bali 5.4. It is a monster sail but surprisingly easy to handle. Andrew listened to our requirements for this downwind sail and built a sail that was ideally suited for our application. A word from our sailmaker at Quantum>>.
Wing-on-Wing Sail Configuration with Dual Headsails
The Code Zero is our favorite sail to use in light winds. It is the most popular cruising multihull downwind sail because they offer great versatility and cover a wide range of wind angles. Today the furling systems used with these sails are great and is as easy to use as a jib. We fly that sail most often and when the wind is just right on the beam, we really get flying. The Code Zero is best used with an AWS (apparent wind speed) of up to 18 knots, with an apparent wind angle (AWA) of less than 135 degrees.
When we blew out our asymmetrical sail halfway across the Atlantic, we were forced to use our head sails and our sailing became somewhat more conservative and a little slower. We set up a wing-on-wing configuration with the Code Zero to one side and the jib out to the other side of the boat. The two sails combine to create one giant sail, and the wind funnels from one sail to another and even though a touch slower than the asymmetrical, was totally adequate and is much more forgiving than sailing wing-on-wing with the headsail and mainsail where you have to use preventers etc. This configuration is also much more manageable and safer to handle for shorthanded crew or a couple.
Autopilot Wind Vane for Downwind Sailing on a Catamaran
When sailing with finicky sail configurations like the ones above, be sure to put your autopilot on wind vane mode and set the wind angle as a priority. That way, if the wind shifts, your autopilot will adjust the boat to have the sails properly filled. If you are running on a heading or a track when the wind shifts, you might find your sails backwinded or do an accidental gibe, which is dangerous.
Being on the wind vane setting does mean that you need to pay extra attention to your course; if the wind shifts, you may have to switch to another downwind sail tactic. Always get the boat balanced and steering comfortably before you switch on the autopilot. If the helm is overpowered and the steering is hard to control when you steer, the autopilot will have the same difficulty keeping a steady course. Set your right combination of sails and trim the sails well to set a comfortable course, then set the autopilot and watch it for a time to make sure it doesn’t labor too hard.
Chafe is Significant on Sails
Sailing downwind across the Atlantic, one will experience a lot of chafe on your running rigging. It’s a huge problem. We had our Code Zero come down while sailing from Madeira to the Canary Islands because the halyard was chafed right through in a few hours. Fortunately, we retrieved the sail without any issues, but it could have been a real problem. One should make provision for chafe and check your lines all the time. In fact, it is good practice to simply roam around the boat and check your running and standing rigging daily while on passage. We have bought several lengths of Dyneema sleeve and have sewn this chafe gear on the wear spots on the spinnaker halyard as well as all the reefing points on the main halyard.
Crash Stop or Quick Stop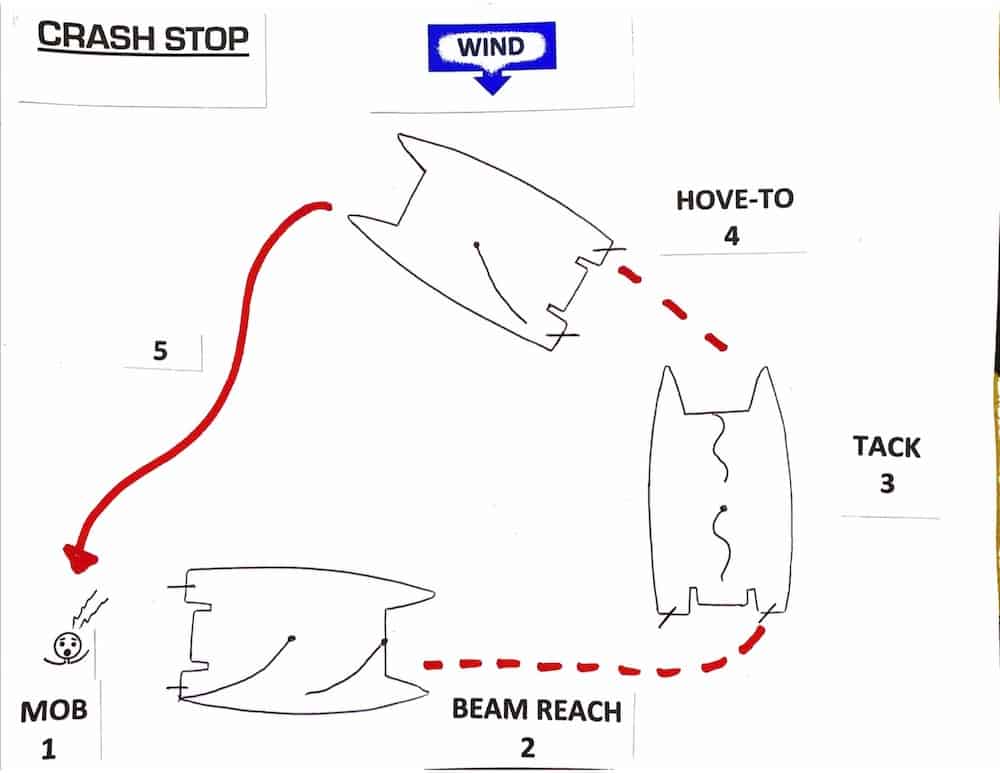
Cruising yachts are mostly sailed by couples and are essentially short-handed. When a crew member goes overboard it is always at the worst possible time and completely unexpected, which means that the reaction time to start the correct maneuver is usually not good. The man overboard recovery method that we prefer being shorthanded, is called the “Crash Stop” or “Quick Stop”. It works in almost all situations and requires only one crew member and no sail trimming. Learn about the MOB Quick Stop Maneuver.
Parking Your Catamaran in Emergency
Parking the boat is an effective method for stopping anywhere and holding station, much like heaving-to in a monohull. Deep reef your main sail, drop the traveler all the way to leeward, and sheet the mainsheet hard in. Secure your helm so the rudders are pushing the boat into the wind. The cat will sit on a close-hauled course, drifting sideways at about ½ knot. This is great if you need a break from very harsh conditions or a squall. The motion will be smooth and will give you time to regroup or effect repairs if necessary.
FYI: If you own a Lagoon, Leopard or Fountain Pajot, you don’t necessarily have to have a sail built for your boat. There are pre-owned sails available to be purchased at a fraction of the cost.
Sail With Us to Learn


Week-Long Liveaboard Courses
Rare RYA Classes & Certifications
Catamaran Guru’s real-life practical methods combined with up-to-date sailing theory in lessons aboard recent model catamarans…or your own boat!
Prepare for certifications or take the first step aboard to embark on your dream life of boat ownership or cruising
Classes in S Florida and the Bahamas.





